No Surgical Backup?
No Problem.
Updated SCAI guidance includes Coronary IVL as a treatment option in all U.S. cath labs regardless of surgical backup status.
SCAI has updated the 2014 Expert Consensus on PCI Without Surgical Backup with new guidance that includes Coronary IVL as a potential therapeutic option in all cath labs - including facilities without on-site surgical backup.1
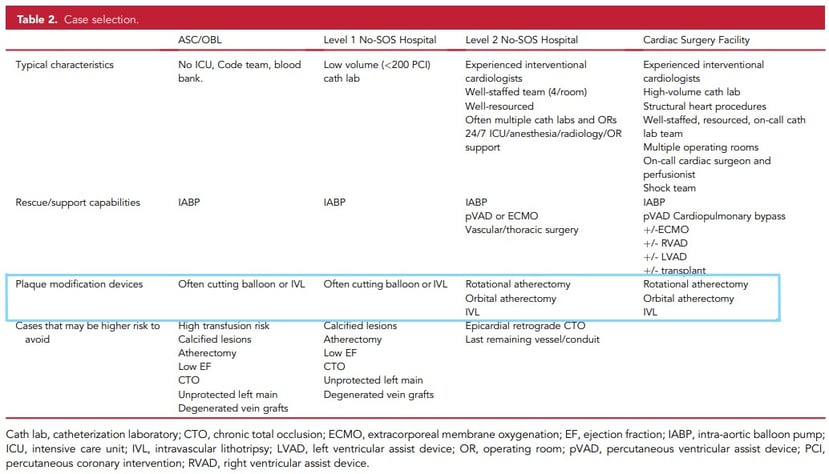
As seen in the table below, SCAI's statement lists IVL as a therapy option across the four different surgical and non-surgical facility types. The updated guidance expands the number of hospitals that can access IVL to include sites where calcium modification tools were previously not recommended. The prior guidance, published in 2014, recommended to avoid the treatment of high-risk lesions defined as “more than moderate calcification” in facilities without surgical backup.2 Authors of the new guidance acknowledged the limitations of the previous guidance:
“…these [prior] recommendations may have restricted practice, limited patient choice, and exposed interventional cardiologists to legal risk. Such prohibitions have become outdated as the skill of interventional cardiologists and technological advances have expanded treatment options, outcomes data show no harm with PCI with no-SOS, and government policies actively encourage moving care to lower-cost areas. In particular, the prohibition of rotational and other atherectomy devices can paradoxically result in increased risk to the patient when balloon angioplasty is attempted in a calcified vessel.”
Operators and administrators working in non-surgical facilities interested in implementing Coronary IVL into their practice may be interested in reviewing the Cath Lab Digest article: Management of Calcified Lesions in Hospitals Without Surgical Backup.
You may also find Coronary IVL product and reimbursement information on the product page and reimbursement page respectively.
Shockwave is proud to play a role in expanding care for patients in facilities without surgical backup through its demonstrably safe, effective and intuitive technology.
- 1. Grines, C. L., Box, L. C., Mamas, M. A., Abbott, J. D., Blankenship, J. C., Carr, J. G., . . . Seto, A. H. (2023, February). SCAI expert consensus statement on percutaneous coronary intervention without on-site surgical backup. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2022.12.016
- 2. Dehmer GJ;Blankenship JC;Cilingiroglu M;Dwyer JG;Feldman DN;Gardner TJ;Grines CL;Singh M;. (n.d.). SCAI/ACC/AHA expert consensus document: 2014 update on percutaneous coronary intervention without on-site surgical backup. Retrieved January 30, 2023, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24637561/
Coronary Important Safety Information:
In the United States: Rx only.
Indications for Use—The Shockwave Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) System with the Shockwave C2 Coronary IVL Catheter is indicated for lithotripsy-enabled, low-pressure balloon dilatation of severely calcified, stenotic de novo coronary arteries prior to stenting.
Contraindications—The Shockwave C2 Coronary IVL System is contraindicated for the following: This device is not intended for stent delivery. This device is not intended for use in carotid or cerebrovascular arteries.
Warnings— Use the IVL Generator in accordance with recommended settings as stated in the Operator’s Manual. The risk of a dissection or perforation is increased in severely calcified lesions undergoing percutaneous treatment, including IVL. Appropriate provisional interventions should be readily available. Balloon loss of pressure was associated with a numerical increase in dissection which was not statistically significant and was not associated with MACE. Analysis indicates calcium length is a predictor of dissection and balloon loss of pressure. IVL generates mechanical pulses which may cause atrial or ventricular capture in bradycardic patients. In patients with implantable pacemakers and defibrillators, the asynchronous capture may interact with the sensing capabilities. Monitoring of the electrocardiographic rhythm and continuous arterial pressure during IVL treatment is required. In the event of clinically significant hemodynamic effects, temporarily cease delivery of IVL therapy.
Precautions— Only to be used by physicians trained in angiography and intravascular coronary procedures. Use only the recommended balloon inflation medium. Hydrophilic coating to be wet only with normal saline or water and care must be taken with sharp objects to avoid damage to the hydrophilic coating. Appropriate anticoagulant therapy should be administered by the physician. Precaution should be taken when treating patients with previous stenting within 5mm of target lesion.
Potential adverse effects consistent with standard based cardiac interventions include– Abrupt vessel closure – Allergic reaction to contrast medium, anticoagulant and/or antithrombotic therapy-Aneurysm-Arrhythmia-Arteriovenous fistula-Bleeding complications-Cardiac tamponade or pericardial effusion-Cardiopulmonary arrest-Cerebrovascular accident (CVA)-Coronary artery/vessel occlusion, perforation, rupture or dissection-Coronary artery spasm-Death-Emboli (air, tissue, thrombus or atherosclerotic emboli)-Emergency or non-emergency coronary artery bypass surgery-Emergency or non-emergency percutaneous coronary intervention-Entry site complications-Fracture of the guide wire or failure/malfunction of any component of the device that may or may not lead to device embolism, dissection, serious injury or surgical intervention-Hematoma at the vascular access site(s)-Hemorrhage-Hypertension/Hypotension-Infection/sepsis/fever-Myocardial Infarction-Myocardial Ischemia or unstable angina-Pain-Peripheral Ischemia-Pseudoaneurysm-Renal failure/insufficiency-Restenosis of the treated coronary artery leading to revascularization-Shock/pulmonary edema-Slow flow, no reflow, or abrupt closure of coronary artery-Stroke-Thrombus-Vessel closure, abrupt-Vessel injury requiring surgical repair-Vessel dissection, perforation, rupture, or spasm.
Risks identified as related to the device and its use: Allergic/immunologic reaction to the catheter material(s) or coating-Device malfunction, failure, or balloon loss of pressure leading to device embolism, dissection, serious injury or surgical intervention-Atrial or ventricular extrasystole-Atrial or ventricular capture.
Prior to use, please reference the Instructions for Use for more information on warnings, precautions and adverse events. https://shockwavemedical.com/IFU
Please contact your local Shockwave representative for specific country availability and refer to the Shockwave C2 instructions for use containing important safety information.

.png?width=294&name=4637coronary%20(3).png)


